The experimental diving bell shown is lowered from rest at the ocean's surface and reaches a maximum depth of 80 m. Initially it accelerates downward at a rate of until it reaches a speed of , which then remains constant. During the descent, the pressure inside the bell remains constant at 1 atmosphere. The top of the bell has a cross-sectional area . The density of seawater is .
(a) Calculate the total time it takes the bell to reach the maximum depth of 80 m.
(b) Calculate the weight of the water on the top of the bell when it is at the maximum depth.
(c) Calculate the absolute pressure on the top of the bell at the maximum depth.
On the top of the bell there is a circular hatch of radius .
(d) Calculate the minimum force necessary to lift open the hatch of the bell at the maximum depth.
(e) What could you do to reduce the force necessary to open the hatch at this depth? Justify your answer.
(a) Calculate the total time it takes the bell to reach the maximum depth of 80 m.
(b) Calculate the weight of the water on the top of the bell when it is at the maximum depth.
(c) Calculate the absolute pressure on the top of the bell at the maximum depth.
On the top of the bell there is a circular hatch of radius .
(d) Calculate the minimum force necessary to lift open the hatch of the bell at the maximum depth.
(e) What could you do to reduce the force necessary to open the hatch at this depth? Justify your answer.
2025.04.30 AP Physics
of the : If you were ruler of your own country what would be the first law you would introduce?
Agenda
Do now
Pascal and Archimedes Principles
Workbook 8.E, F & G
Finish for Homework
Goals
Model Buoyant Force
Upcoming
2025.04.29 AP Physics
of the : What superstition do you think is ridiculous?
Agenda
Pressure Notes
AP Workbook 8.C & 8.D
Goals
Model Pressure
Upcoming
2025.04.25 AP Physics
of the : If you could teleport inside any game, which would it be?
Agenda
Pressure vs. Depth Pivot
Pressure Notes
AP Workbook 8.C & 8.D
Goals
Develop mathematical model for pressure
Upcoming
2025.04.24 AP Physics
of the : How many pairs of shoes do you own?
Agenda
Finish Density Workbooks
Under Pressure Notes
Pressure vs. Depth Lab - Pivot
Goals
__
Upcoming
2025.04.23 AP Physics
of the : Would you rather be able to see infrared or ultraviolet light?
Agenda
Notes on Fluids
AP Workbook 8.A & 8.B
If Time - Unit 6 Workbook continued
Goals
Define Fluid
Define Density
Upcoming
2025.04.21 AP Physics
of the : Would you rather understand the complete history of Earth or the complete future of humanity?
Agenda
Notes on Oscillations
AP Workbook on Oscillations - Unit 6 - Start and see how far you get
Goals
Define Simple Harmonic Motion
Upcoming
Lab Report Due
Fact Sheet Quizzes, Fact sheet to be updated today
2025.04.11 AP Physics
of the : What is your favorite fast food chain?
Agenda
Oscillations Lab
Due Wednesday we return from break...I was hopeful that you finished in class today...
Goals
FInish Oscillation Lab
Block
Start
End
Block 4
11:39
12:39
Assembly
12:39
2:00
2025.04.08AP Physics
of the :
Agenda
Oscillations lab
Goals
Model the period of an oscillation
Upcoming
Lab Report Due Friday
2025.04.07 AP Physics
of the : What was the last movie you went to? What did you think?
Agenda
Oscillations lab
Goals
Model the period of an oscillation
Upcoming
Lab Report Due Friday
Oscillations Lab
Experimental Question
What factors affect the period of oscillation for your system (pendulum or spring mass system)?
What is the mathematical relationship between those variables and the period of oscillation?
Hypthosis
What do you know from physics (forces, energy, kinematics, momentum) etc that can help predict this motion?
i.e. if you set up an energy bar graph does mass matter?
2025.04.04 AP Physics
of the : If gravity suddenly decreased by half for 24 hours, what would you do first?
The figures below show hollow spheres (not drawn to scale) that are rolling at a constant rate without slipping. The
spheres all have the same mass, but their radii as well as their linear and angular speeds vary.
Forces Test Wednesday before break. AP Classroom is open.
2024.12.05 AP Physics
of the : What is the best board game?
Agenda
Do Now: AP Workbook 2.J
Examples on Solving Atwood Machines
AP Workbook 2.I
Old AP Exam Questions - Paired Problem Solving on Whiteboard
Goals
Model accelerating systems
Upcoming
2024.12.04 AP Physics Do Now
The two blocks are identical and both are at rest. A student comparing the normal force exerted on the block by the surface in the two cases states:
“Since both blocks are identical, I think the normal forces are the same because in each case the normal force will be equal to the weight.”
What, if anything, is wrong with this contention? If something is wrong, identify it and explain how to correct it. If this contention is correct, explain why.
2024.12.04 AP Physics
of the : What is your favorite Disney movie?
Agenda
Do Now
AP Workbook 2H
Incline Plane AP Derivations
Friction Paragraph Question (AP Classroom)
Solving Two Body Systems (AP Workbook 2.J & 2.K)
Goals
Solve Inclined Plane Problems
Upcoming
A box is being pushed at constant speed up an inclined plane to a vertical height of 3.0 m above the ground. The person exerts a force parallel to the plane. The mass of the box is 50 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the plane is 0.30.
Draw and label the forces (not components) acting on the box.
Calculate the normal force of the plane on the box.
Calculate the component of the force of gravity acting on the box that is parallel to the plane.
Calculate the friction force between the plane and the box.
Calculate the force applied by the person on the box.
An empty sled of mass 25 kg slides down a muddy hill with a constant speef of 2.4 m/s. The slope of the hill is inclined at an angle of 15 with the horizontal.
Calculate the time it takes the sled to go 21 m down the slope.
Draw and label a free-body diagram for the sled as it slides down the slope.
Calculate the frictional force between the sled and the slope.
Calculate the coefficient of friction between the slope and the sled.
The sled reaches the bottom of the slope and continues on the horizontal ground. Assume the same coefficient of friction.
i. In terms of velocity and acceleration, describe the motion of the sled as it travels on the horizontal ground.
ii. Sketch the velocity vs. time graph for the sled. Include the sled's travel down the slope and across the horizontal ground. Indicated wtih the symbol the time at which the sled leaves the slope.
A box of mass is at rest on a inclined plane at an angle of . Derive an expression for the coefficient of friction between the box and the ramp in terms of the given variables and any universal constants.
A person exerts a force on a rope to pull a block of mass up a ramp. The rope makes an angle to the ramp and the ramp makes an angle to the horizontal, as shown. The force of kinetic friction between the block and the ramp has a magnitude . Which of the following expressions is equal to the magnitude of the acceleation of the block?
A.
B.
C.
D.
2024.12.02 AP Physics
of the : What is your ideal burger (or veggie burger)?
Use the graphic organizer to set up the question, then solve question asked
Goals
Solve Force problems with angles
Upcoming
2024.11.20 AP Physics
of the : Is your glass half full or half empty?
Agenda
Finish Friction Lab
Solving Friction Problems
With Porter
Start Homework Problems
Goals
Solve N2L Problems involving Friction
Upcoming
N2L Quiz tomorrow, no angled forces
2024.11.19 AP Physics
of the : What’s your favorite sandwich and why?
Agenda
Friction Lab
Problem-solving friction questions
Goals
Experimentally measure coefficient of friction
Applying Friction to N2L
Upcoming
N2L Quiz Thursday
2024.11.15 AP Physics
of the : Which person in your life is most likely to secretly be a time traveler?
Agenda
Fact Sheet Quiz - 15 Minutes
Friction Notes
Friction Lab Introduction
Make Lab Report Pretty (Last 20 Min)
Goals
Model Friction
Upcoming
Definitely a Forces Quiz next week, N2L, mass vs. weight, etc
2024.11.14 AP Physics
of the : How long would you be able to last withouth your smart devices (phone, computer, watch, etc)? 1 Hour? 1 Day? 1 Week?
Agenda
Spring Force Lab
Friction Lab
Goals
Model Spring Force
Model Friction
Upcoming
Fact Sheet Quiz Tommorow
Lab Report Due Tomorrow
2024.11.13 AP Physics Do Now
A person who weighs 500 N is standing on a scale in an elevator. The elevator is identical in all cases. The velocity and acceleration of the elevators at the instant shown are given.
List the cases where the scale reading is greater than 500 N.
List the cases where the scale reading is less than 500 N.
List the cases where the scale reading is equal to than 500 N.
Rank the scale reading from greatest to least.
2024.11.13 AP Physics
of the : What slang are you really happy went out of fashion?
Agenda
Do Now Warmups
Peer Edits on Lab Reports (20 min)
Spring Force Lab
Goals
Solve problems with angled forces
Upcoming
Fact Sheet QuizFriday
Sign up for kinematic reassessments...
Peer Edits
Intentions:
What do you want your partner to focus on when reading your lab report?
Feedback:
What glows about the lab?
Where is room to grow?
Provide Feedback referencing the lab report rubric
Peer Edit Feedback
What did you learn from your partner's lab?
What challenges did you face when providing feedback?
What do you plan on changing about your lab report?
What questions do you still have for Mr. Porter?
Spring Force Lab:
Objective:
Determine the relationship between stretch and force applied on a spring. Test this relationship for two springs
(Note: When analyzing graph Spring Force on the vertical axis regardless of your experimental design choice on independent variable)
Available Materials:
Two different springs
Spring Scales (force sensors)
Masses
Ruler/Meterstick
Electronic Force Sensor
2024.11.07 AP Physics
of the : What animal do you think is the creepiest?
Agenda
Quiz and Quiz Buffet
Solving N2L for angled questions
Goals
Solve N2L with angled forces
Upcoming
2024.11.06 AP Physics
of the : If you were to open a store, what would you sell?
Agenda
Force of Gravity
Solving N2L Problems Systematically
Goals
Solve problems using N2L
Upcoming
Buffet Quiz Tomorrow (Thursday) -> pick you non-mastered standards to reassess
Gravity:
Notes:
Weight == == Force of Gravity...so
Weight is a FORCE, mass is scalar quantity
is the gravitational field strength
Measured in N/kg
changes based on planet and location on that planet
near the surface of the Earth
You can round this to
2024.11.01 AP Physics
of the : If you were one of Snow White’s dwarfs, which one would you be?
Agenda
Finish Data Analysis on Lab
Whiteboard Results
Board Meeting - Do your results support N2L?
Goals
Evaluate Newton's Second Law with lab data
Upcoming
Test Corrections Due 11/07
2024.10.31 AP Physics
of the : What was your favorite Halloween costume?
Agenda
Finish Collecting Unbalanced Force Lab Data
Board Meeting - Unbalanced forces, mass, and acceleration
Goals
Discover mathematical model for unbalanced forces.
Upcoming
Test Corrections Due: 11/08
2024.10.29 AP Physics
of the : Who is the most competitive person you know?
Agenda
Finish Unbalanced Force Fan Cart Lab
Whiteboard and Present Results
Goals
Discover mathematical model for unbalanced forces.
Upcoming
Test Corrections Due: 11/08
2024.10.28 AP Physics Do Now
A 0.5-kg ball is suspended from a ceiling by two strings. The ball is at rest.
(a) Is the tension in string 1 (i) greater than, (ii) less than, or (iii) the same as the tension in string 2?
Explain your reasoning.
2024.10.28 AP Physics
of the : What smell brings back great memories?
Agenda
Do Now
Fan Cart N2L Lab
Test & Test Correction Process
Goals
Create a mathematical model between force and acceleration
Upcoming
Test Corrections - Notes and FAQs
Usually about a week to complete
You cannot do them at home or outside of the classroom (AP Police will find us)
No I will not tell you what you did before
You may come work during study hall -> But I will not be able to help you if I have a class.
take your test and work on it in the breakout space outside of my classroom, or in the middle room.
Curve is
Test Corrections
Determine correct answer for incorrect questions
For FRQ you need to correct the entire part (i.e. part (a)) if you lost any points
No you cannot see what you put before - start from scratch
For MC questions you must provide a justification
Start with a fact of physics "slope of VT is acceleration" or "area of VT is displacement"
Draw a diagram to help (i.e. draw a VT graph)
Try to use a claim evidence reasoning format to write your justification
Finally, compare your new, correct answers to your test and determine if your mistake was one of the 4 C's: clueless, careless, conceptual, or calculation.
Test Corrections Summary
Look for trends about what your test performance:
Were there certain types of questions you missed?
Do you need to review/relearn/learn some material that was tested?
What learning mastery standard do you think that material aligns with?
Was there a common mistake you made?
Summarize
Meet with Mr. Porter to discuss the trends before you turn in your corrections.
2024.10.22 AP Physics Do Now
The forces exerted on an object at a particular instant are represented in the free-body diagram. The magnitude of each force is drawn to scale. A student claims that the vector sum of the forces on the object is equal to zero. Is the student’s claim valid? Why or why not?
2024.10.22 AP Physics
of the : What’s the best pizza topping?
Agenda
Do Now
FBD Card Sort
Practice with FBDs
Solving Balanced force problems with FBDs
Goals
2.2.B Describe the forces exerted on an object or system using a free-body diagram.
of the : Would you rather watch a movie on your TV at home or on the big screen in the theater, and why?
Agenda
T/F Simulation -> Share out
Rules for CV vs. CA Motion
Force Diagrams and Defining Forces
Goals
Draw Diagrams to represent force situations
Identify forces acting on object
Upcoming
Test Wednesday, HW This week -> Finish AP Classroom work
2024.10.17 AP Physics
of the : If you found that food was falling from the sky, what food would you want to be falling? What food would you NOT want to be falling?
Agenda
Quiz
Mallet Ball Summary & Simulation True/False
Dynamics Laws
Goals
Define laws of physics describing motion
Upcoming
Test 10/23 -> Complete Review!
2024.10.16 AP Physics
of the : Would you rather have invisibility or flight?
Agenda
Mallet Ball
Goals
__
Upcoming
2024.10.15 AP Physics
of the : You can have an unlimited supply of one thing for the rest of your life, what is it? Sushi? Scotch Tape? (You can't say money or anything related to money)
Agenda
Finish Relative Motion Pivot
Notes: Vectors and adding Vectors
Pivot: Adding Vectors
Goals
Add 2D Vectors
Upcoming
Quiz Thursday on Projectile Motion & Relative Motion
Kinematics Test 10/23
2024.10.10 AP Physics
of the : What is your favorite type of apple?
Agenda
Quiz
Frames of Reference
Relative Motion Pivot
Relative Motion Workbook Problem: 1.E
Physics Classroom Practice
Goals
Define Frames of Reference
Solve problems involving relative motion
Upcoming
2024.10.09 AP Physics Do Now
Check you answers to the homework ranking task with your table.
Whiteboard your collective answer
2024.10.08 AP Physics
of the : Vacation on the beach or adventure in the mountains?
Agenda
Do Now
Projectiles at an angle
Turd the Target
Notice!
AP PAYMENT DUE 10/17 to Guidance
Goals
Solve projectile motion problems
Upcoming
Quiz tomorrow
Expect graphs, equations, freefall, and a horizontal projectile question
2024.10.08 AP Physics
of the : You have to sing karaoke, what song do you pick?
Agenda
Introduction to Horizontal Projectiles
Marble Mini Lab
Goals
Solve horizontally fired projectile problems
Upcoming
Quiz Thursday -> Free fall and projectiles
2024.10.04 AP Physics
of the : What skill or talent do you most want to learn?
Agenda
Quiz
Finish Free Fall Pivot
AP Workbook 1.J & 1.K
Projectile Motion Introduction
Horizontally Fired Projectiles
Goals
Define a projectile and solve projectile motion problems
Upcoming
2024.10.01 AP Physics Do Now
A Car is moving with constant speed when a tree falls into the roadway at . It takes the driver a time to react and apply the brakes. The car then slows with a constant acceleration of magnitude . Which of the following equations correctly expressed the distance traveled by the car from to the instant the car comes to rest?
A.
B.
C.
D.
A Car is moving with constant speed when a tree falls into the roadway at . It takes the driver a time to react and apply the brakes. The car then slows with a constant acceleration of magnitude . Which of the following equations correctly expressed the distance traveled by the car from to the instant the car comes to rest?
C.
Combine
and
2024.10.02 AP Physics
of the : What secrets do you think your pet would spill about you, if they could talk?
Agenda
Do Now
Free Fall Five
Free Fall Notes
Free Fall Practice
Rocket Science
AP Workbook 1.J, 1.K
Physics Classroom
Goals
Solve problems involving Freefall motion
Upcoming
Quiz Friday
Stacks of graphs
Solving word problems, potentially two stage motion
2024.09.30 AP Physics
of the : What household chore do you actually enjoy?
Agenda
Finish Practice
Intro to Motion Sensors
Free Fall Motion
Physics Classroom Free Fall
Goals
Solve kinematic problems graphically and with equations
2024.09.27 AP Physics Do Now
A biker speeds up to 31.3 m/s from rest in 6.10 seconds. The biker maintains this speed for 6.35 seconds before coasting to a stop in 8.4 seconds. What was the biker's average speed for the trip?
Solve this BOTH Graphically and with Equations
2024.09.27 AP Physics Do Now
At time , a moving cart on a horizontal track is at position . Using a motion sensor, students generate a graph of the cart's velocity as a function of time, as show to the right. At , the cart's position is most nearly
2024.09.27 AP Physics
of the : If you came with a warning label what would it say?
Agenda
Do Now
Predict the split lab practical
Goals
Use VT Graphs to solve problems
2024.09.26 AP Physics
of the : If you came with a warning label what would it say?
Agenda
Quiz - Shapes of Graphs
Finish Bear Problem & Discuss
Kinematic Equations & Cross Diagram
Using Kinematics Equations and graphical problem solving
of the : Would you rather be a dragon or own a dragon?
Agenda
Graphical Problem Solving
Coming Up...
Thursday: Shapes of Graphs Quiz
Friday: Fact Sheet Quiz
Goals
Use VT Graphs to solve problems
2024.09.23 AP Physics
of the : If animals could talk which would be the most annoying?
Agenda
VT Graphs
Problem Solving
Goals
Create a mathematical model for motion
Describe different physical quantities
Relate stacks of kinematic graphs
2024.09.20 AP Physics
of the : What animal would you want for a non-traditional pet? (i.e. not a dog, fish or cat)
Agenda
Chart Summary Discussion
Notes
Card Sort Round 2
Quantitative VT Graphs
Goals
Create a mathematical model for motion
Describe different physical quantities
Relate stacks of kinematic graphs
2023.09.18 AP Physics Do Now Take 2
The position-time graph shown represents the motion of two children who are moving along a narrow, straight hallway.
Do either of the children ever change direction?
Are the two children ever at the same position along the hallway?
Do the two children ever have the same speed?
Do the two children ever have the same acceleration?
2024.09.18 AP Physics
of the : Which of the five senses would you say is your strongest?
Agenda
Card Sort Activity
Acceleration Notes
Card Sort #2
Goals
Create a mathematical model for motion
Describe different physical quantities
Relate stacks of kinematic graphs
2024.09.17 AP Physics
of the : If one superhero was real, which one should it be?
Agenda
Fan Cart Lab:
Linearize (Review)
Discuss
Wrap Up Lab Notes
Changing Speed Notes
Card Sort Activity
Goals
Create a mathematical model for motion
Describe different physical quantities
Homework
Due Friday, Posted on canvas
2023.09.16 AP Physics Do Now
The position-time graph shown represents the motion of two children who are moving along a narrow, straight hallway.
Do either of the children ever change direction?
Are the two children ever at the same position along the hallway?
Do the two children ever have the same speed?
Do the two children ever have the same acceleration?
2024.09.16 AP Physics
of the : Would you rather travel 100 years forward or back in time?
Agenda
Do Now
Fan Cart Lab:
Collect Data
Graph on Pivot
Sketch Graph(s) on whiteboard
Data analysis discussion
Board Meeting & Notes
Goals
Create a mathematical model for motion
Describe different physical quantities
Homework
Due Friday, Posted on canvas
2024.09.12 AP Physics Do Now
Describe a motion that has
the same distance, displacement, and final position
different distance, displacement, and final position
Describe a real-life situation where it is important to consider velocity as a vector
2024.09.12 AP Physics
of the : Do you have any weird/unique routines or superstitions? (For example: I have to put on my left sock before my right sock, and the same for shoes, left on first.)
Phone number to reach your parents/guardians if you sleep through the AP Exam
Favorite Candy
Favorite Emoji
Emoji the describes your current mood
Fill out Paper Quesionnaire
Lab Grouping Game
There are 8 of you and 8 extra cards
Based on your cards get into LOGICAL pairs with two extra cards
Check whole class answer with Mr. Porter
4 Chances to Check
Reorganize if necessary
(Yes this is the game Connections)
Survival Island
Share your survival skill that you wrote down with your group
Using everyone's skill develop a plan to survive or escape the deserted island
On your whiteboard present your plan (drawing, mind map, set of instructions)
Highlight everyone's skill
Surivial Plan...
Buggy Lab
Objective:
Determine if your toy buggy moves in a consistent manner by developing a relationship between position and time.
Use time as your independent variable
Lets Science!
Lab Notebooks
What is a Lab Notebook?
A detailed, chronological record of a scientist's research activities, experiments, and observations.
Documentation of the scientific process from intial ideas to final results and conclusions.
Why keep lab notebooks?
Document Research
Develop Ideas
Organize Data
Collaboration Tool
Publication Support
Troubleshooting
Intellectual Property Protection
Historical Record
Lab Notebooks can be Legal Documents
Proof of invention in Patent Cases
Intellectual Property Protection
Admissibility in court - must be properly maintained
Note: Often property of the instituation where the research was conducted (i.e. Property of Regeneron, or Property of Cornell University)
Remember
Lab notebooks are most importantly scientific documentation
They represent the scientific process and are record of your thinking
This means your ideas and conclusions and hypotheses can change based on new data
Lab Notebook
Write in pen
All mistakes get a single cross through
Full Date (YYYY/MM/DD) at the beginning of each entry (for multiday labs date start of each day)
Enter Lab Pages into table of contents
Lab Notebook - Pre Lab
Title and objective of the experiment:
Write a clear, concise title for each experiment.
State the main objective or purpose of the experiment in 1-2 sentences.
*Theoretical background:
Briefly explain the relevant scientific principles.
Include key equations or concepts that will be tested or applied.
Hypotheses:
State your predictions about the experiment's outcome.
Base these on your understanding of the theory.
Lab Notebook - Pre Lab
Materials and equipment list:
Provide a detailed list of all materials and equipment used.
Include model numbers and specifications where relevant.
Experimental procedure outline:
Write a step-by-step outline of the planned procedure.
Be specific enough that someone could replicate your experiment.
During the Experiment
Raw data in tables with units:
Create neat, organized tables for all numerical data.
Always include units and uncertainty estimates.
Label columns clearly and use consistent significant figures.
Observations and qualitative notes:
Record all relevant observations, even if they seem unimportant.
Note any unexpected occurrences or anomalies.
Any changes to the planned procedure:
Document any deviations from the original procedure.
Explain why changes were made and how they might affect results.
Sketches or diagrams of experimental setup:
Include clear, labeled diagrams of your experimental setup.
Add dimensions and important details to aid in replication.
Post Lab
Data analysis and calculations:
Show all steps in your calculations, including formulas used.
Explain your reasoning for each step of the analysis.
Graphs and charts:
Create neat, properly labeled graphs and charts.
Include titles, axis labels with units, and legends where appropriate.
Post Lab
Discussion of results:
Interpret your results in the context of the experiment's objectives.
Explain any patterns or trends observed in the data
Comparison with hypotheses:
Explicitly state whether your results support or refute your hypotheses.
Discuss possible reasons for any discrepancies.
Sources of error and uncertainty:
Identify potential sources of experimental error.
Discuss how these might have affected your results.
Quantify uncertainties where possible.
Post Lab
Conclusions:
Summarize the main findings of the experiment.
Relate these back to the original objectives and broader scientific principles.
Suggest improvements or future directions for the experiment.
Buggy Lab
Objective:
Determine if your toy buggy moves in a consistent manner by developing a relationship between position and time.
Use time as your independent variable
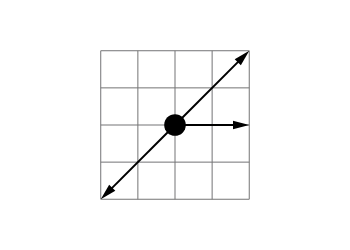
Identical treasure chests (shown from above) each have two forces acting on them. All chests start at rest.
**Rank the speed of the treasure chest after 2 seconds.**
---
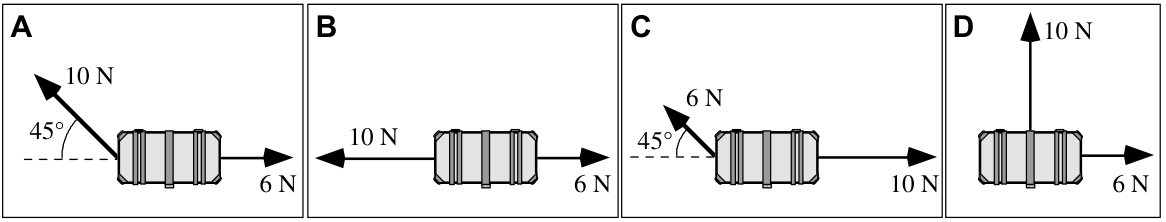
The forces exerted on an object at a particular instant are represented in the free-body diagram. The magnitude of each force is drawn to scale. A student claims that the vector sum of the forces on the object is equal to zero. Is the student's claim valid? Why or why not?
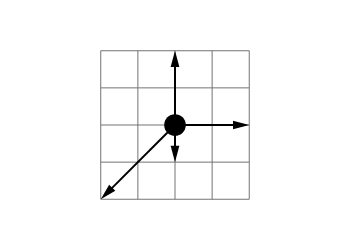
---
The free-body diagram shows three forces exerted on an object. Each square is 1 N by 1 N. What is the magnitude of the vector sum of the forces exerted on the object?