Self Check
Complete solo and check with table
Self Check 

During their physics field trip to the amusement park, Tyler and Maria took a ride on the Whirligig. The Whirligig ride consists of long swings which spin in a circle at relatively high speeds. As part of their lab, Tyler and Maria estimate that the riders travel through a circle with a radius of 6.67 m and make one turn every 8.21 seconds. Determine the speed of the riders on the Whirligig.
Self Check 

A toy airplane makes 74 revolutions about its 91.8-cm radius circle in 1 minute. Determine the speed of the plane.
Speed
Imagine you are a lady bug standing on a record player
How does the distance from the center of the circle affect your speed?
Centripetal Acceleration
The acceleration of an object moving in a circular path.
Centripetal Acceleration
The acceleration is directed towards the center of the circle
Centripetal Acceleration
Self Check 

What is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of a car following a curve of radius 500 m at a speed of 25.0 m/s (about 90 km/h)? Compare the acceleration with that due to gravity for this fairly gentle curve taken at highway speed.
Self Check 

What is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of a car following a curve of radius 500 m at a speed of 25.0 m/s (about 90 km/h)? Compare the acceleration with that due to gravity for this fairly gentle curve taken at highway speed.
Self Check 

A barrel rider is moving in a circle with a speed of 8.0 m/s. The acceleration of the rider is 7.2 m/s/s. The speed of the object is somehow increased to 16.0 m/s (i.e., doubled). The new acceleration would be _____ m/s/s. (Assume that the radius of the circle is not changed.)
Self Check 

Eva and Harper buy tickets for the barrel ride at the local carnival. The barrel has a radius of 7.08 m. Eva and Harper experience an acceleration of 9.65 m/s/s once they get up to speed. Calculate the …
- … the speed at which they are moving.
- … the time for the barrel to make one complete revolution.
Self Check 

Avery plays the young David in his church's play on David and Goliath. Avery is practicing with his 0.667-m long sling and finds that he can rotate it in a circle at 8.34 revolutions/second. But if he increases the length to 0.975 m, he is able to rotate at a less impressive 5.36 revolutions/second.
- Calculate the acceleration of the sling when swung at 8.34 rev/s.
- Calculate the acceleration of the sling when swung at 5.36 rev/s.
 Pause to Practice
Pause to Practice
Physics Classroom Practice
Spinning Stoppers
- Twirl stopper around head
- Decrease/Increase radius and notice what happens to the tension.
- Decrease/Increase twirling speed - what happens to the tenion?
- If you were to increase the mass how do you think that would impact the tension?
Centripetal Force
- "Center Seeking Force" - The net force that causes an object to move in a circle.
- It is a special name for net force or the sum of all of the radial forces (forces along the radius of the circle) NOT AN ACTUAL FORCE
- The net force that causes motion in a circular path
- Alters the direction of motion without altering the speed.
Again...
The word “centripetal” refers to a direction and that it is always some external force, such as the normal force, gravitational force friction, or tension, exerted centripetally that allows an object to execute circular motion.
Why do the following move in circles?
What force or forces are keeping the object moving in a circle?
Centripetal Force Examples...
As a car makes a turn, the force of friction acting upon the turned wheels of the car provides centripetal force required for circular motion.

Centripetal Force Examples...
As a bucket of water is tied to a string and spun in a circle, the tension force acting upon the bucket provides the centripetal force required for circular motion.

Centripetal Force Examples...
As the moon orbits the Earth, the force of gravity acting upon the moon provides the centripetal force required for circular motion.

Centripetal Force Equation
- Newton's Second Law
- Newton's Second Law for Circular Motion
- We know
Centripetal Force Equation
- Newton's Second Law
- Newton's Second Law for Circular Motion
- We know
Example
The maximum speed with which a 945-kg car makes a 180-degree turn is 10.0 m/s. The radius of the circle through which the car is turning is 25.0 m. Determine the force of friction and the coefficient of friction acting upon the car.

Example
The coefficient of friction acting upon a 945-kg car is 0.850. The car is making a 180-degree turn around a curve with a radius of 35.0 m. Determine the maximum speed with which the car can make the turn.
Some Proportions
- For constant mass and radius, how is speed related to Centripetal force?
- For constant speed and mass, how is the radius related to the Centripetal force?
- For constant speed and radius, how is mass related to the net force?
Summary
- Velocity is tangent to the circle and calculated with
- Centripetal acceleration is towards the center of the circle and a calculated with
- Centripetal Force is the sum of the radial forces (net force) and is calculated with
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
Wait what about
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
Calculate
- Mass of Earth =
- Mean radius of Earth =
Yo! it is about 9.8 N/m! I recognize that number!
Practice Calculation
Determine the Force of gravity between the Earth and the Moon:
- Earth's Mass:
- Moon's Mass:
- Distance Betwen Earth and Moon:
- Earth's Radius:
- Moon's Radius:
At the instant shown, three asteroids are in a line, and the distance between A and B is twice the distance between B and C. Asteroid C has mass
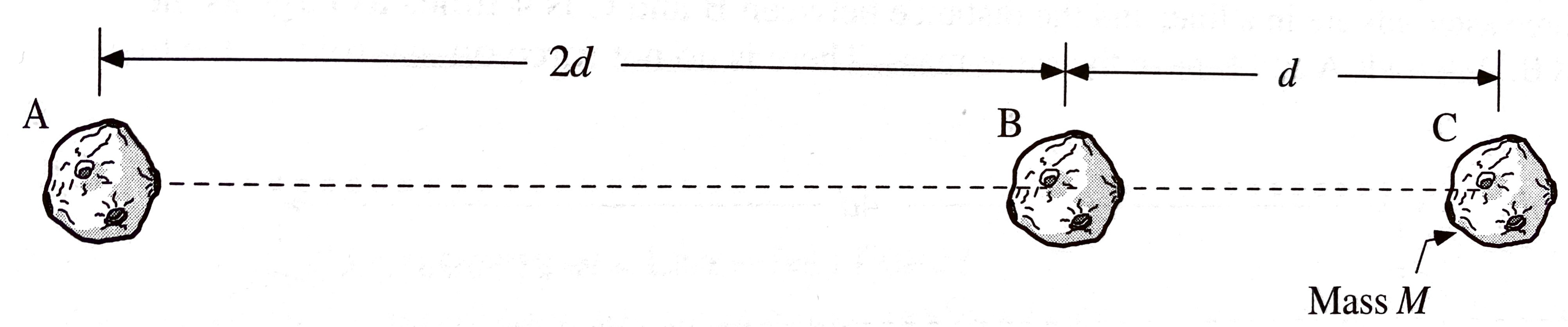
Three students are discussing how they might find the mass of asteroid A:
Ari: "We don't really have enough information to find the mass of A. Since there's no net force on B, the force from A has to cancel the force from C. To find the force on B from C, we'd use Newton's law of Universal Gravitation. But since the force is proportional to the produce of the masses we'd need to know both masses."
Bira: "I don't think we really need the mass of B. Asteroid A is twice as far away as C, so if it also has a mass M it will exert half has much force as C does. Since it has to exert the same force for the net force on B to be zero, it has to have twice the mass."
Cole: "It's true that A pulls on B to the left, and C pulls on B to the right, But you can't just use Newton's law of universal gravitation, because that only allows you to calculate the force between the two masses. here there are three masses, and asteroid A is exerting some of its force on B and some on C."
With which, if any, of these students do you agree?