Mathematical Models
General Mathematical Mode:
Specific Mathematical Model (example):
Narrative Model:
"The toy car started at a position of 250 cm and moved in the positive direction at a speed of 25 cm/s."
Defining "How Far"
Who went further? Dorothy or Toto?
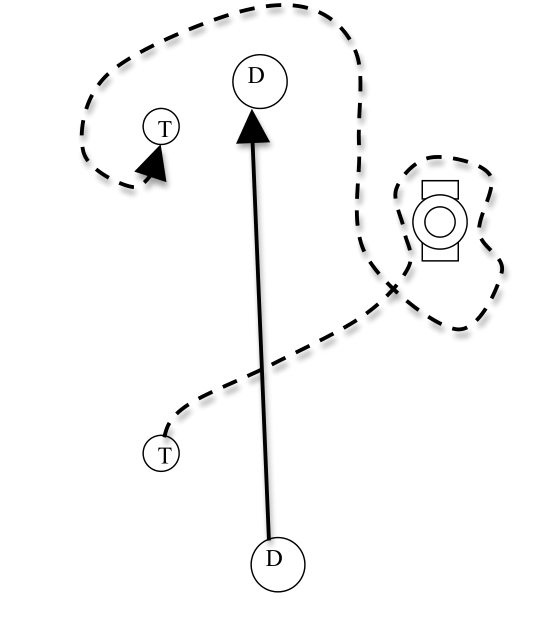
Displacement
- Change in position of an object
- Includes direction
Distance
- the magnitude (or size) of displacement between two positions
- more often referred to as distance traveled which is the total length of the path traveled between two positions
Position
- Where an object is at any particular time
- "Location"
CER in AP Physics:
-
Claim:
- Sentence that answers the question.
-
Evidence:
- Explanation of how the evidence supports the claim.
- Should include details!
- Refer back to the question, include any data, diagrams, or graphs.
- Explanation of how the evidence supports the claim.
-
Reasoning:
- Physics principle, such as an equation, law, or definition.
- This is general, do no include specific details.
- Physics principle, such as an equation, law, or definition.
Game: Soup, Salad, or Sandwich
- Write a Claim-Evidence-Reasoning statement arguing whether the shown food is a soup, salad, or a sandwich.
Soup, Salad, or Sandwich?
Soup, Salad, or Sandwich?
class: invert
Soup, Salad, or Sandwich?
Soup, Salad, or Sandwich?
CER
Does the object in the image move with a constant velocity?
Motion Maps - Represent this pictorially:
Motion Maps
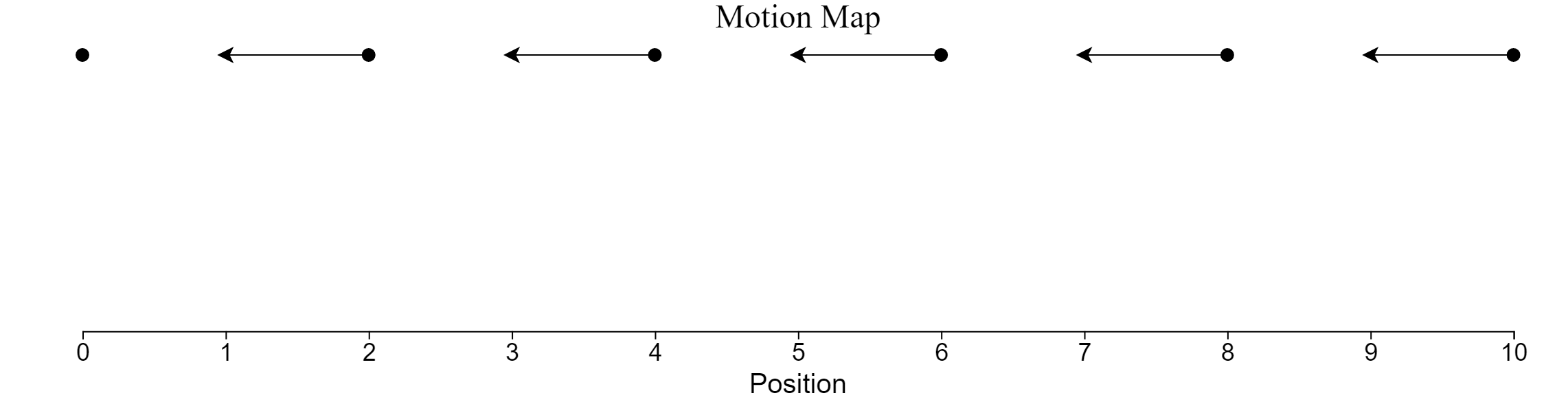
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
Try it...
.png)
.png)
Practice: Complete individually and compare
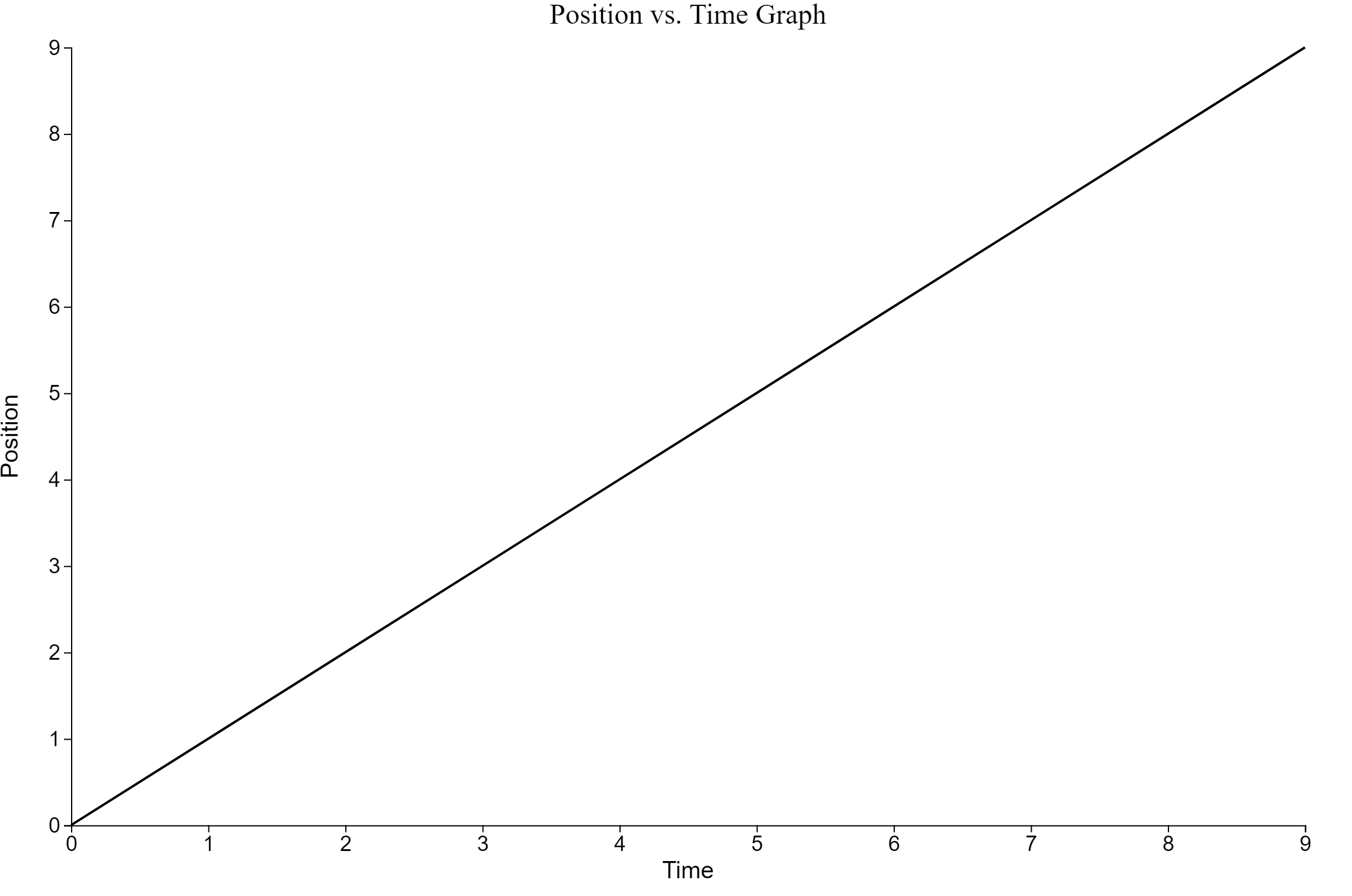
Given the following position vs. time graph
- Draw a motion map with one dot for each second
- Describe the motion in worsds
More Practice
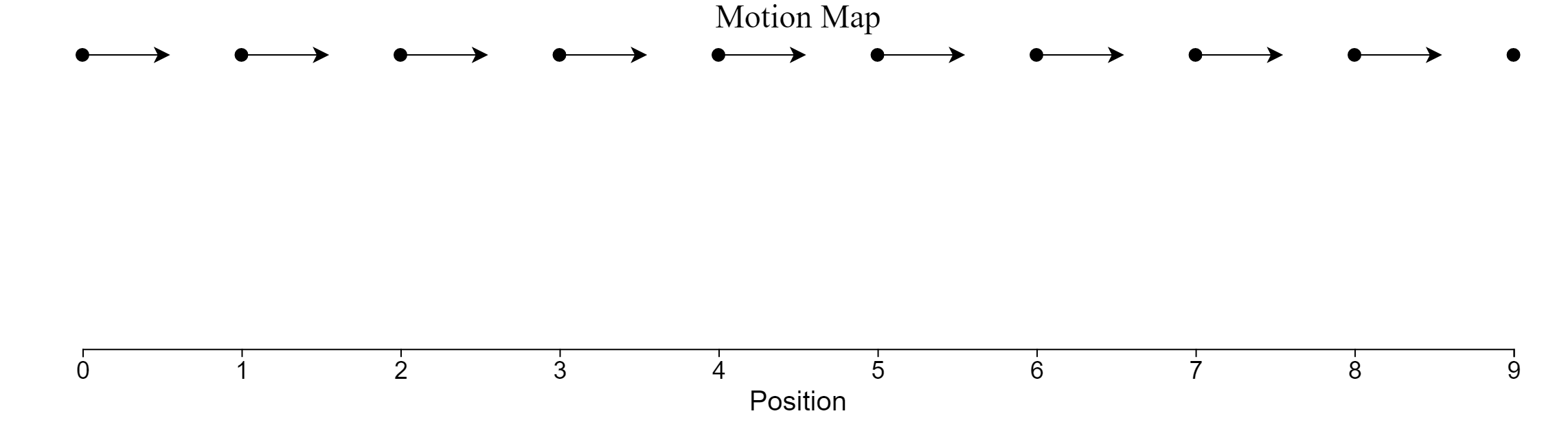
Given the following motion map, where positions have been recorded with one dot each second,
- Draw a position vs. time graph
- Describe the motion of the object in words
Motion Sensor Lab
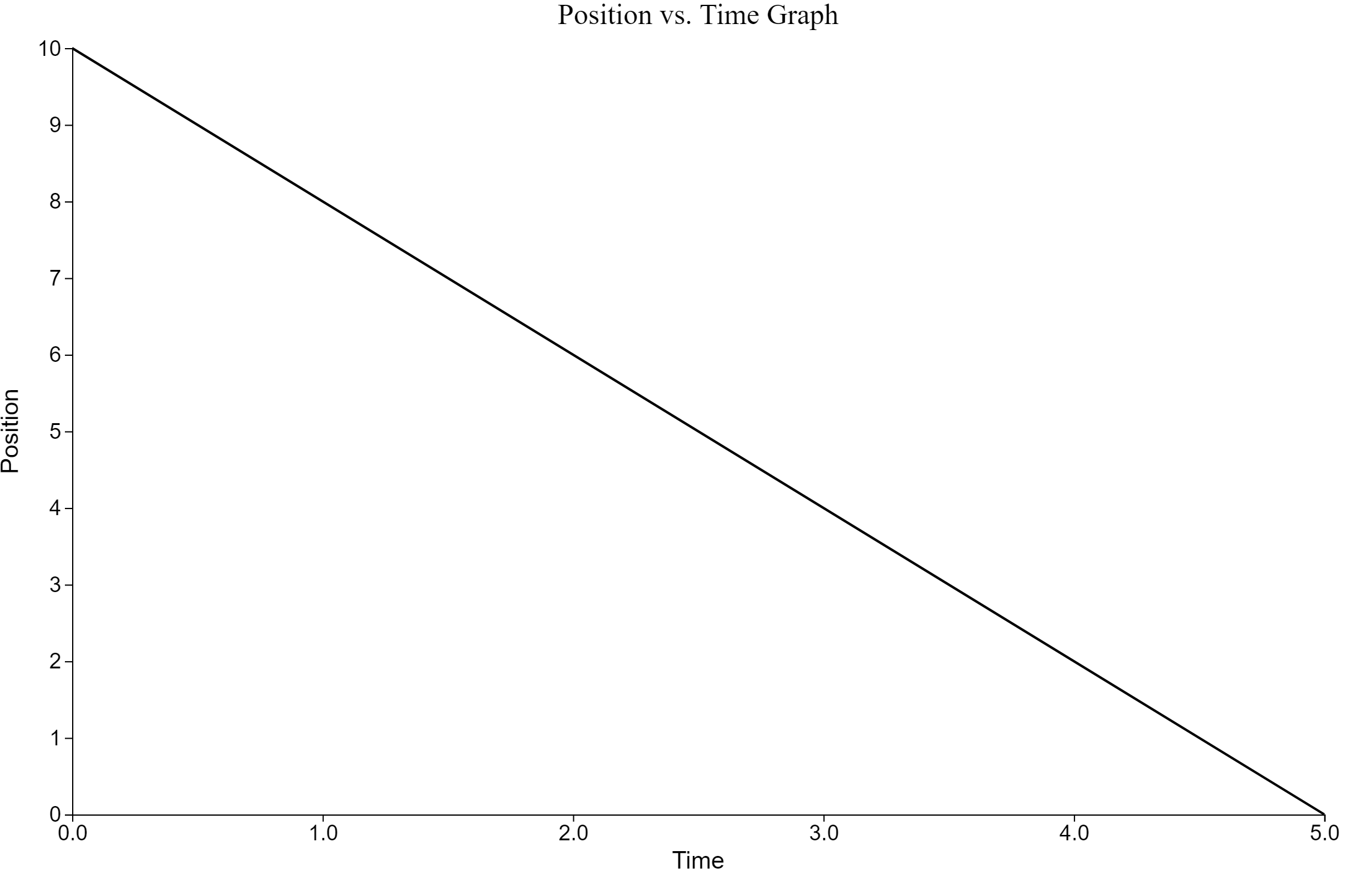
Analyzing Position-Time (XT) Graphs
For the following position vs. time graph, consider the positive direction to be north.
- When is the object moving North? South?
- When is the object stopped?
- When is the object North of the origin?
- What is the velocity of the object at
Analyzing Position-Time (XT) Graphs
- When does the object change directions?
- What is the total distance the object travels?
- What is the total displacement of the object?
- What is the average velocity of the object?
- What is the average speed of the object?
Average Velocity
Dispalcement divided by the change in time.
"The average slope of the graph"
Average Speed
Total distance divided by change in time
Instantaneous Values:
- "at that moment"
- Value at a specific time
Instantaneous Velocity
- Velocity at a specific time
- The slope of the position vs. time graph at that time measurement
Instantaneous Speed
- Magnitude of the velocity
Mathematical Modeling & Making Predictions
Constant Velocity Particle Model
final position
constant velocity
time
initial position
A racecar reaches a speed of 95 m/s after it is 450 meters past the starting line. If the car travels at a constant speed of 95 m/s for the next 12.5 seconds, how far will the care be from the starting line?
- Sketch and label the situation
- Physics diagrams: position vs. time graph, motion map (qualitative)
- Mathematically model
- Solve
Mr. H waits patiently as two beetles race across the 35.8-cm length of the cereal box. According to Mr. H's estimates, Beetle A averages 0.230 cm/s and Beetle B averages 0.454 cm/s. Beetle A has a 4.1-cm 'head start' (when Beetle B is at the far edge of the box). What is the separation distance (in cm) between beetles when the first beetle reaches the end of the box?
- Sketch and label the situation
- Physics diagrams: position vs. time graph, motion map (qualitative)
- Mathematically model
- Solve
Velocity vs. Time Graphs
VT Graphs
- Draw the velocity vs. time graph for an object whose motion produced the position vs. time graphs shown below.
- For many graphs, both the slope and area between the line and the horizontal axis have physical meanings. What does the slope of the position vs. time graph tell you about the motion of an object?
VT Graphs
- Complete the following chart and show your work
| Area "under the curve" of VT Graph | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 |
VT Graphs
- Looking at the velocity vs. time graphs, determine the units for a square of area on the graph.
- What does the "area under the velocity-time graph" tell you about the motion of the object?
Area of VT Graph
- Area "under the curve" represents the displacement (change in position) of the object.
- Areas can be negative because that represents the direction
- Add multiple segments together, including the sign to get the total displacement of a piecewise motion
Area of VT Graph
- Area =
- Area =
- Area =